In the landscape of economics, the concept of a natural monopoly stands as a unique phenomenon, shaping industries and challenging conventional market structures. Unlike traditional monopolies, which arise from anti-competitive behavior or market manipulation, natural monopolies emerge from the inherent characteristics of certain industries. These industries exhibit cost structures that make it more efficient to have a single firm providing the entire output, leading to a single dominant player in the market.
Defining Natural Monopoly
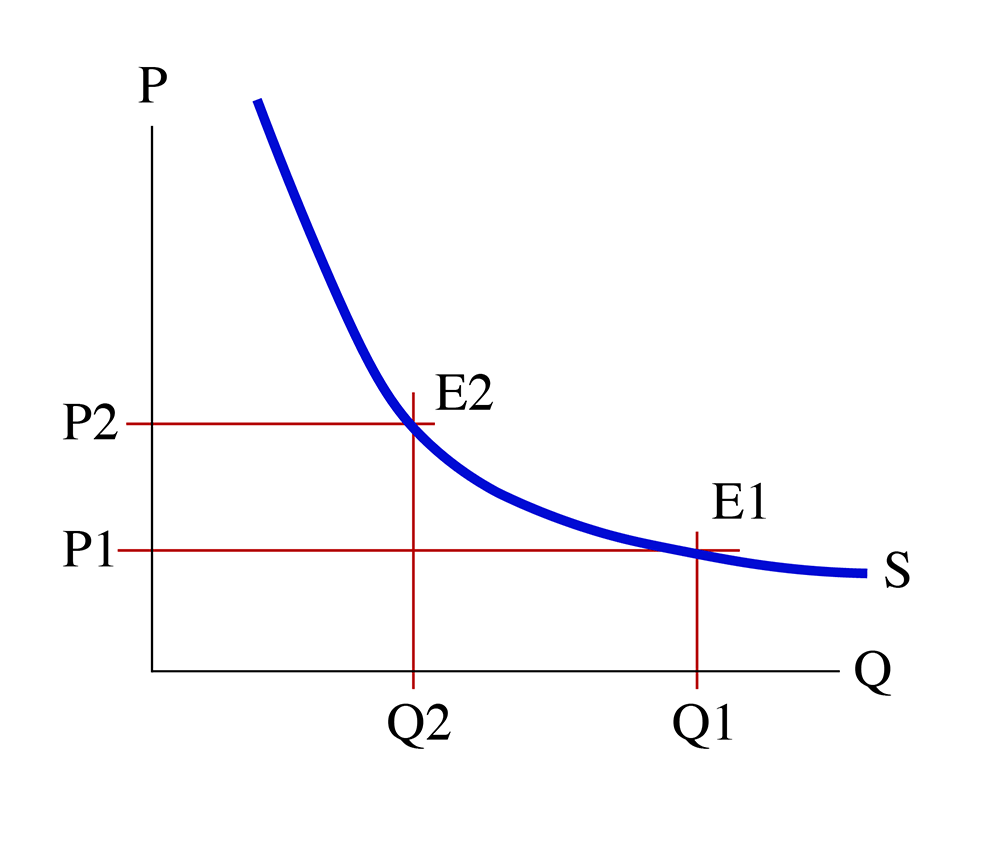
At its core, a natural monopoly occurs when the average cost of production continuously decreases as the scale of production increases, allowing a single firm to serve the entire market at the lowest possible cost. This phenomenon typically arises in industries with high fixed costs and low marginal costs, such as utilities , transportation infrastructure and telecommunications.
Characteristics of Natural Monopolies
Economies of Scale
Natural monopolies benefit from economies of scale, where the cost per unit of output decreases as production increases. This makes it financially impractical for multiple firms to enter the market and compete effectively.
High Fixed Costs
The initial investment required to enter the market and establish infrastructure is prohibitively high, serving as a barrier to entry for potential competitors.
Technological Advancement
Technological advancements can enhance the efficiency of natural monopolies, further solidifying their dominance. For instance, advancements in telecommunications have enabled faster transmission speeds and broader coverage, consolidating the market power of major telecom companies.
Benefits and Challenges
Benefits
Efficiency
Natural monopolies can achieve optimal efficiency by avoiding duplication of infrastructure and benefiting from economies of scale, ultimately leading to lower prices for consumers.
Innovation
With fewer competitors, natural monopolies can focus on long-term investment and innovation without the pressure of immediate market competition.
Challenges
Lack of Competition
The absence of competition may lead to reduced incentives for innovation and quality improvements, as the monopolist faces little pressure to enhance its products or services.
Market Power Abuse
Without proper regulation, natural monopolies may abuse their market power by charging excessive prices or providing poor-quality services.
Regulatory Approaches
Given the complexities surrounding natural monopolies, regulatory intervention is often necessary to strike a balance between efficiency and consumer protection. Several regulatory approaches can be adopted:
Price Regulation
Regulators can impose price controls to prevent monopolies from charging unfair prices. This can involve setting price caps or implementing profit margin restrictions to ensure affordability for consumers.
Quality Standards
Regulatory agencies can establish minimum quality standards to ensure that monopolies maintain satisfactory service levels. This can include requirements for reliability, safety, and customer support.
Open Access
In certain industries, such as telecommunications and energy, regulators may mandate open access to infrastructure to encourage competition in downstream markets. This allows multiple service providers to utilize the same infrastructure, promoting innovation and consumer choice.
Anti-Competitive Practices Monitoring
Regulatory bodies must actively monitor monopolistic behavior to prevent anti-competitive practices such as predatory pricing, collusion, or market foreclosure.
Conclusion
Natural monopolies represent a complex economic phenomenon that requires careful consideration and regulatory oversight. While they offer potential benefits in terms of efficiency and innovation, unchecked monopolistic power can harm consumers and stifle competition. Therefore, policymakers must implement robust regulatory frameworks to ensure that natural monopolies operate in the best interests of society, balancing the need for efficiency with the imperative of consumer protection. By striking this balance, societies can harness the advantages of natural monopolies while mitigating their potential drawbacks, fostering a competitive and dynamic economic environment.





